From Tricks to Transformation: The 3 Stages of AI Adoption for MSPs
Every MSP's AI journey begins the same way. Someone on the team tries ChatGPT for the first time, marvels at its ability to write emails in the style...
Get everything you need for the ultimate client experience
Enterprise-grade infrastructure with the flexibility MSPs demand
Perfectly tailored AI that knows your specific MSP

Build your own Shopify-like store with your PSA products & distributors
Have clients to submit tickets directly to your PSA, freeing up your team's time
Pre-triage and route tickets correctly with the help of AI
Deliver instant, accurate answers that can help achieve zero-touch resolution
You'll learn things like how to add revenue without adding cost, MSP best practices, and how to master client management.
7 min read
 CloudRadial
:
January 22, 2026
CloudRadial
:
January 22, 2026
Every MSP's AI journey begins the same way. Someone on the team tries ChatGPT for the first time, marvels at its ability to write emails in the style of a pirate, and suddenly everyone's talking about using AI for everything. But six months later, that same enthusiasm often fades into doubt as teams struggle to move beyond novelty applications to create real business value.
This pattern isn't unique to MSPs—it's happening across industries as organizations grapple with the gap between AI's promise and its practical implementation. The challenge isn't that AI lacks transformative potential; it's that most businesses get stuck in the early stages of adoption, never progressing to where AI can fundamentally reshape how they operate.
Understanding the three distinct stages of AI adoption can help MSPs navigate this journey more strategically, avoiding common pitfalls while building toward implementations that don't just improve efficiency—they redefine what's possible for service delivery.
The first stage of AI adoption is characterized by experimentation and wonder. Team members discover they can ask AI to write emails in different tones, generate creative content, or solve abstract problems in entertaining ways. This phase serves an important purpose—it demystifies AI and builds familiarity with the technology—but it rarely delivers measurable business value.
In MSP environments, this might look like using AI to write more colorful incident reports, generate witty out-of-office messages, or create team-building content. While these applications can boost morale and demonstrate AI's versatility, they don't address core operational challenges or client needs.
The fundamental problem with staying in the tricks phase is that novelty wears off quickly. What seems impressive initially becomes routine, and without clear business applications, AI tools get abandoned. Teams may conclude that AI is "overhyped" or "not ready for serious business use," missing the opportunity to explore more valuable implementations.
Many MSPs plateau here because they lack a framework for identifying practical applications or because early experiments don't produce obvious ROI. Without proper guidance, it's easy to dismiss AI as a technological curiosity rather than recognizing it as a stepping stone toward more sophisticated uses.
The key to progressing beyond this stage is shifting focus from entertainment to utility. Instead of asking "What can AI do that's interesting?" the question becomes "What repetitive or time-consuming tasks could AI handle more efficiently?" This mindset shift opens the door to the productivity stage, where AI begins delivering tangible business value.
The productivity stage represents AI's sweet spot for most current implementations. Here, AI tools become practical assistants that help teams work faster, communicate more effectively, and handle routine tasks with greater consistency. The focus shifts from novelty to measurable gains in efficiency and output quality.
In the productivity phase, MSPs typically implement AI for tasks like drafting client communications, generating technical documentation, creating knowledge base articles, and analyzing log files for common issues. These applications deliver clear time savings and often improve the quality of outputs by providing structure, consistency, and professional polish.
For example, instead of spending 30 minutes crafting a detailed incident report, a technician might use AI to generate a comprehensive draft in 3 minutes, then spend 5 minutes reviewing and customizing it. The net result is a 20-minute time saving plus a more thorough, professionally written report.
One of the most impactful productivity applications is automated documentation generation. AI can analyze support interactions to create troubleshooting guides, identify documentation gaps, and generate client-specific procedural documentation. This addresses one of MSPs' biggest operational challenges while creating valuable assets for future use.
Similarly, AI-powered search and recommendation systems help technicians quickly find relevant information during support incidents. Instead of manually searching through documentation repositories, technicians can describe their current situation and receive contextually relevant resources, procedures, and historical solutions.
While the productivity stage delivers real value, it also represents a natural plateau for many organizations. Teams achieve meaningful efficiency gains and improved output quality, but they're still fundamentally doing the same work—just faster and better. AI remains a tool that enhances human work rather than transforming how work gets done.
This stage is characterized by linear improvements: faster ticket resolution, better documentation, more consistent client communications. These gains are valuable and measurable, but they don't fundamentally change business models or create new competitive advantages.
The question becomes: what's next?
The intelligence stage represents a fundamental shift in how MSPs use AI—moving from task automation to operational visibility and strategic insight. This is where AI transitions from being a productivity tool to becoming a diagnostic and analytical system that reveals patterns humans simply cannot see across thousands of tickets, hundreds of technicians, and dozens of clients.
For MSPs ready to progress beyond productivity gains, the opportunity lies not in replacing human decision-making, but in illuminating blind spots that have always existed in service delivery operations.
The most transformative aspect of AI isn't automation—it's analysis at scale. Every MSP has years of ticket data containing invaluable patterns about technician performance, client satisfaction, documentation quality, and operational efficiency. But that data has historically been too voluminous and unstructured for meaningful analysis.
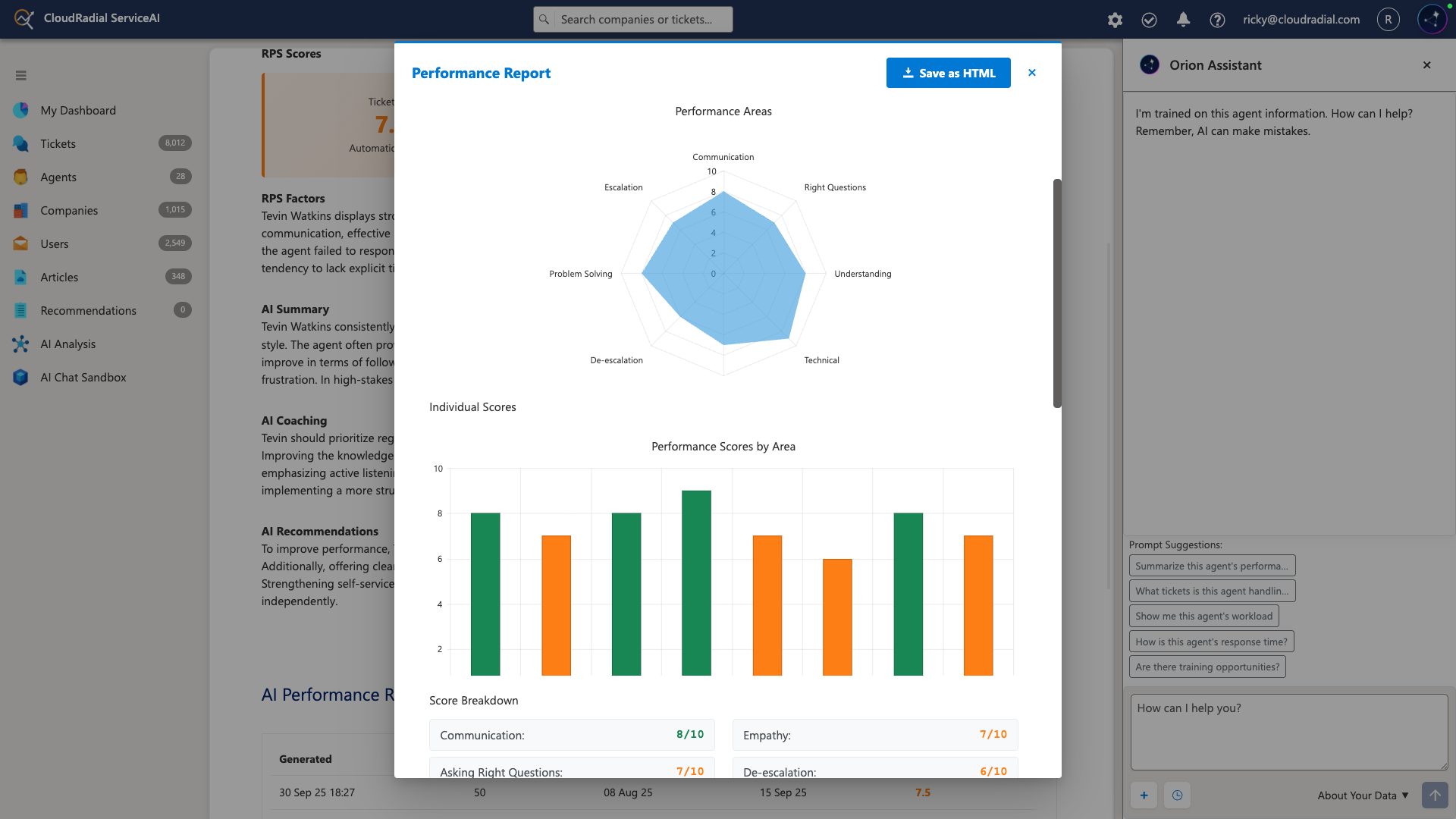
AI-powered intelligence platforms can evaluate every ticket response your team has ever written, score them for quality, empathy, and clarity, and identify both your top performers and those who need coaching. This isn't productivity—this is visibility into your operations you've never had before.
At the intelligence stage, AI helps MSPs answer questions that were previously impossible to address:
Which technicians consistently provide high-quality responses? AI can analyze communication patterns, resolution approaches, and client interactions to identify your strongest performers and understand what makes them effective.
Which clients have the most complex support needs? By scoring tickets and analyzing patterns, you can identify clients consuming disproportionate resources and understand why.
Where are the gaps in your documentation? AI can identify tickets with low confidence scores, indicating areas where better documentation would improve future resolution.
What's the root cause behind recurring issues? Trend analysis across tickets reveals patterns by category, product, or client that point to systemic problems worth addressing.
This intelligence doesn't resolve tickets automatically—it empowers service desk managers to make better decisions about coaching, staffing, client management, and process improvement.
The intelligence stage also enables MSPs to prepare their teams more effectively. Instead of waiting for problems to reveal themselves through client complaints or extended resolution times, AI analysis identifies coaching opportunities, documentation needs, and process gaps before they impact service quality.
For example, an AI system might flag that tickets related to a specific software platform consistently receive low quality scores, indicating technicians need better training or documentation in that area. Or it might identify that certain clients consistently express frustration in their tickets, signaling a relationship that needs attention.
This isn't predictive maintenance or automated problem prevention—it's informed preparation. AI surfaces the insights; humans take the action.
A critical principle at the intelligence stage is maintaining human control over all client-facing decisions. AI-powered systems can suggest ticket responses based on historical patterns and documentation, but technicians review, edit, and decide what to send. The human remains in control of customer communication.
This collaborative model delivers value in two ways:
When a technician rates an AI suggestion as unhelpful, that feedback flags the interaction for service desk managers to review, leading to documentation improvements, rule adjustments, or training opportunities. Over time, the quality of suggestions improves—not through automated machine learning, but through human-guided refinement.
While AI shouldn't make client-facing decisions without human oversight, it can handle routine operational tasks with confidence. Intelligent triage systems can automatically route incoming tickets to the correct boards and queues, categorize them appropriately, assign them to the right technicians, and flag priority keywords for immediate attention.
This automation frees dispatchers and service desk managers from repetitive sorting work, allowing them to focus on complex cases and relationship management. And because these systems can operate in testing mode first, MSPs can validate the AI's logic before deploying it to production.
One of the most valuable aspects of the intelligence stage is the ability to validate AI behavior before exposing it to clients or technicians. Sandbox environments let MSPs test how AI would respond to specific scenarios, impersonate different companies and users to see contextual responses, and identify documentation gaps in a safe environment.
This capability addresses one of MSPs' biggest concerns about AI: "What if it gives a wrong answer to a client?" By battle-testing responses before deployment, you can ensure quality and build confidence in AI-assisted service delivery.
At the intelligence stage, MSPs gain access to metrics that productivity tools don't provide:
These metrics don't just measure how fast work gets done—they measure how well it's being done, and where improvements would have the greatest impact.
The distinction between productivity and intelligence isn't just about better metrics—it's about fundamentally different questions:
Productivity asks: "How can we do this work faster?"
Intelligence asks: "What work should we be doing differently?"
MSPs that reach the intelligence stage don't just have faster ticket resolution—they have deeper insight into their operations, more effective coaching programs, better-prepared teams, and stronger client relationships informed by data they never had access to before.
The distinction between productivity and intelligence requires fundamentally different approaches to AI implementation. While general-purpose AI tools excel at productivity applications, achieving operational intelligence requires specialized systems designed specifically for service delivery contexts.
Purpose-built AI platforms for MSPs focus on learning from your specific historical data, providing visibility into your unique operations, and helping prepare your teams for AI-assisted service delivery. These systems don't just help MSPs work more efficiently—they provide insight into how service desks actually perform, where improvements would have the greatest impact, and how to deploy AI safely.
The question for every MSP isn't whether to adopt AI, but how quickly they can progress through the three stages to reach intelligence before their competitors do. The MSPs that master AI-powered operational insight will define the future of managed services, while those that remain stuck in earlier stages risk being left behind.
The journey from tricks to intelligence isn't always linear, and different parts of an organization may be at different stages simultaneously. However, understanding these phases provides a roadmap for strategic AI adoption that maximizes value while avoiding common pitfalls. For MSPs ready to move beyond productivity gains toward genuine operational intelligence, the opportunity has never been greater—but the window for competitive advantage won't remain open indefinitely.

Every MSP's AI journey begins the same way. Someone on the team tries ChatGPT for the first time, marvels at its ability to write emails in the style...
Your service desk manager pulls up the dashboard and smiles. Response times are faster. More tickets handled per technician. Documentation time...

The Service Desk Visibility Gap As an IT Service Manager, you face a challenge that generic productivity tools can't solve: you don't actually know...